The use of telemedicine, or remote clinical consultations, was limited in most countries before the pandemic, held back by regulatory barriers and hesitancy from patients and providers. In early 2020, as COVID‑19 massively disrupted in-person care, governments changed the playfield and acted decisively and broadly to promote the use of this discipline.
Consequently, the number of teleconsultations reached unprecedented numbers, playing a vital role in maintaining access to care, but it wasn’t enough to offset reductions in face-to-face care. This is one of the conclusions reached by a recent study published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), entitled “The COVID-19 Pandemic and the Future of Telemedicine“.
The document also proposes policy priorities for using telemedicine in the near future like learning more about which patients are using remote care services, why they are using these services and what happens after they use them. It is as well highlighted the need to investigate whether telemedicine payment and prices are creating economic signals and incentives that promote value for money. Finally, foster integration between remote and in-person care services is needed so that these are fully coordinated and part of a seamless care pathway.
Telemedicine before the SARS-CoV-2
Prior to the pandemic, nine countries (Estonia, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, Türkiye and the United States) allowed only in-person medical consultations. While it was possible to use telemedicine services in other states, many governments had specific requirements to telemedicine that effectively disincentivised its use. And although the number of services was growing in territories such as Australia, Canada and Portugal, teleconsultations were only between 0.1% and 0.2% of all appointments, according to the study.
Among the nations that participated in the OECD Survey on Telemedicine and COVID‑19, 23 out of 31 are currently allowing teleconsultations to be performed by health workers other than doctors, six more that before the pandemic (Estonia, Germany, Iceland, Luxembourg, Portugal and the United States).
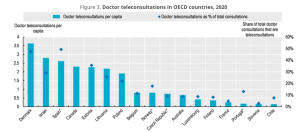
Doctor teleconsultations in OECD countries, 2020. / OECD
Despite the rapid adoption of policies to promote the use of telemedicine, only seventeen countries state that rules and regulations governing the provision of telemedicine services are well established and clear.
An uncertain future
During the pandemic, eight countries (Belgium, Czech Republic, England, Estonia, Hungary, Korea, Latvia and Luxembourg) have begun paying for teleconsultations through government/compulsory schemes, and other eight (Belgium, England, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Latvia and Switzerland) have done the same for remote patient monitoring services.
However, many of the changes that have enabled greater use of teleconsultations during the pandemic are temporary and have not become permanent. For example, in sixteen OECD countries, changes to regulations are transitory and subject to ongoing or periodic review, just like changes regarding financing in twelve states.
Given the circumstances, it is unclear whether remote care substitutes for or complements in-person care, and whether telemedicine adds value when it does not deliver extra benefits and could be replaced with cheaper alternatives with identical or better outcomes.
Reference:
OECD. “The COVID-19 Pandemic and the Future of Telemedicine”. OECD Publishing (2023)
![]() Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or HaDEA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or HaDEA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.



